Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and subcutaneous (fat below the skin) tissues. If unchecked, it can progress and extend to involve other normal tissues and pose a serious threat to the patient. However, in the early stages of its development, cellulitis can be effectively and completely treated by a plastic surgeon.
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection with the involvement of skin and subcutaneous tissues. Subcutaneous tissues include the fat and loose areolar tissues below the skin. In early stages of cellulitis presents itself as a patch of red, swollen and tender skin. If treated with proper antibiotic, cellulitis subsides without producing any undesirable effects. However, after progression to certain level, cellulitis leads to tissue destruction and when treated with antibiotics at later stage, it results in to suppuration (formation of pus). Pus thus formed within the tissues needs to be drained by a plastic surgical operation called debridement. Debridement does not only mean removal of pus, but it involves complete removal of all dead, infected, potentially dangerous tissues along with complete removal of pus and other infected tissue flakes. When cellulitis happen to an immunocompromised patient or elderly and frail patients, it can rapidly progress to involve the whole body. This involvement of whole body by cellulitis process is called as systemic sepsis and it requires intensive care and can lead to death of the patient.
Hand cellulitis presents itself as swelling, pain and redness. The most important instruction for the patient of hand cellulitis is elevation of the hand apart from other necessary treatment measures. Unfortunately, this basic concept of hand elevation for the treatment of hand cellulitis is not prevalent and many patients of hand cellulitis end with chronic edematous, stiff and non-functional hand.
Cellulitis of leg is the most commonly occurring cellulitis. All age group patients are affected from leg cellulitis. However, diabetic patients, aged patients, patients with varicose veins, patients with lymphatic edema have repeated episodes of cellulitis due to low vitality of their tissues. Treatment of leg cellulitis needs to be done under constant and long-term supervision of a plastic surgeon. Half hearted or inadequate treatment of leg cellulitis predisposes the patient to most dreaded sequelae called lymphedema.
Cellulitis of face is not so common, because face is having the highest vascularity (blood supply) in our body. However, folliculitis or infection of hair follicles inside the nose is a very painful condition and can sometimes lead to cellulitis of adjacent lip, cheek and face. Penetrating injuries or injuries by a contaminant object can lead to cellulitis of face which require hospital admission and aggressive treatment.
Perianal cellulitis is not uncommon. This condition usually results from infection of hair follicle (folliculitis) and after treatment with proper antibiotic, like cellulitis in other parts of the body, perianal cellulitis results in suppuration (pus formation) and results into an abscess. This abscess is drained under anesthesia and after few dressings and follow up visits, everything heals. This is not always the case in perianal cellulitis, Perianal cellulitis can be the result into fistula (abnormal communication) in the anal canal. It is called fistula in ano and it requires to be treated by an expert gastroenterologist surgeon.
Common symptoms of cellulitis are pain, swelling and redness with tenderness of affected area. Symptoms vary up to certain extent according to the involved area. Cellulitis of leg and hand causes more swelling than other body parts and it responds well to elevation. Cellulitis of face particularly nose and adjacent regions is very painful condition.
If unchecked, cellulitis can extend to the proximal (higher) areas of upper or lower limbs and can lead to systemic spread of infection. This condition is called systemic sepsis. The symptoms of systemic sepsis are variable, but if they are ignored or missed, they can cost a patient’s limb or life. Symptoms of systemic sepsis include decreased urine output, high-grade fever, increased rate of breathing (tachypnea), easy fatiguability, weakness, or, in the late stages, altered sensorium of the patient. Along with these, the progression of the cellulitis continues to involve other normal areas without any evidence of resolution in systemic sepsis.
Causes of cellulitis are trivial. Most common cause of cellulitis is infection of a hair follicle called folliculitis. Other causes include insect bite, mosquito bite, thorn prick or nail prick injury, penetrating injury by any object, minor to moderate burn injury, small cuts of skin or such seemingly minor injuries. However, cellulitis can start spontaneously also especially in patients of old age, patients with diabetes, anaemia, thyroid edema, patients having chronic (long standing) edema of legs due to any reason and immunocompromised patients.
If treated in early stages of its development with proper antibiotic, cellulitis resolves without causing any problem. However, if treatment is delayed after progression of cellulitis, it results in tissue destruction (necrosis) with pus formation (abscess) and this compels to do a plastic surgical operation of debridement (removal of dead and infected tissues) and drainage of pus. Complications of cellulitis which is progressed to advanced level can be disastrous. After progression to very advanced level, cellulitis process tends to push bacteria into bloodstream, leading to most disastrous sequelae called systemic sepsis. Systemic sepsis requires multidisciplinary approach and treatment in an intensive care unit. In spite of all efforts, patients of systemic sepsis are at risk of death, especially if they develop a condition called septic shock.
Prevention of cellulitis in the early stages of its development is a straight forward phenomenon. If a patient presents to a plastic surgeon during the very early stage of the development of cellulitis, only 3 to 5 days of treatment with suitable oral antibiotics can completely resolve the cellulitis. However, delay in treatment or the presence of virulent bacteria in affected tissues makes the treatment complicated.
At Cutis Hospital, all O.P.D. patients are consulted and examined in detail by an experienced plastic surgeon. Based on his vast clinical experience of managing such cases, our plastic surgeon suggests the best treatment for the patient of cellulitis. Surgical treatment for cellulitis like incision and drainage of pus and debridement are effectively carried out without delay. Some patients of cellulitis require reconstruction of their tissue defect later on. Starting from simple to complex reconstructions, reconstruction of lower limb, hand, trunk, face or any part of the body is carried out very efficiently at Cutis hospital by our plastic surgeon. Not only that, after reconstruction, post operative care, physiotherapy and rehabilitation of the patient is closely followed by our plastic surgeon himself. Patient and his/her relatives are counselled at each stage of treatment and special counselling is done by our plastic surgeon for prevention of cellulitis in patients who are at risk of development of repeated cellulitis.
Thus, Cutis hospital provides complete, comprehensive care for the whole spectrum of cellulitis and at Cutis, we make sure about total rehabilitation of our patients and prevention of their cellulitis.

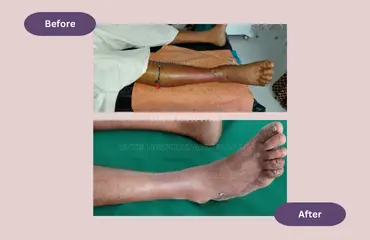
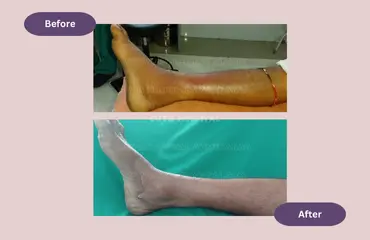
Development of repeated cellulitis is usually the result of hair follicle infection (folliculitis). Low hygiene level of particular body parts can also cause repeated cellulitis. Undiagnosed diabetes or immunocompromised conditions can also predispose to cellulitis.
If caused by a very low virulent bacteria, sometimes cellulitis can heal by itself. In majority of cases, treatment is required in the form of antibiotic therapy.
Yes, we itch sometimes during cellulitis. Itching is more noticeable in the resolution stages of cellulitis due to presence of inflammatory cells and their mediators (chemicals).
No, cellulitis is not contagious. However, pus discharge from the cellulitis affected skin might have presence of bacteria and it should be considered a potential contaminant.
In early stages, cellulitis resolves within 3 to 5 days with proper antibiotic therapy. However, after moderate progression, cellulitis might require an intervention by a plastic surgeon and then the recovery might be delayed up to 2 to 3 weeks or more. Advanced disease process can retard recovery for months.
You should immediately consult a plastic surgeon after noticing initial signs of cellulitis such as pain, redness and swelling.
Cutis Hospital is conveniently located in Ghatlodia, Ahmedabad, making it easily accessible via multiple modes of transportation. Below are the various ways you can reach our facility:
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport: Located approximately 12.7 km from Cutis Hospital, offering convenient access for patients traveling from outside the city.
Chandlodiya Railway Station: Approximately 2.4 km from Cutis Hospital.
Ahmedabad Railway Station: Around 11 km from our center.
GSRTC:
Ahmedabad Central Bus Station (GSRTC): About 10.3 km from the hospital.
AMTS:
Bhuyangdev Cross Road Bus Stop: Just 500 meters from Cutis Hospital.
BRTS:
Bhuyangdev BRTS Bus Stop: Only 170 meters from our center.
We provide effective surgical and non-surgical treatments for all parts of the body. At Cutis Hospital, our cosmetic and plastic surgery team is committed to giving patients safe and high-quality care.