Certain body parts, such as the hands, have a higher risk of getting infected through viruses or bacteria. The hand is a complex structure; even a slight injury, such as a minor cut, might result in an infected hand. Individuals with chronic medical conditions such as diabetes or people with weak immune systems are at a higher risk of developing an infection in the hands.
Hand infections are common and can affect people despite their age group. There are several sorts and causes of hand infections, due to which there are different types of treatments too. Moreover, it is essential to remember that hand infections can have long-term or permanent complications if not treated properly.
Hands play a significant role in lives and most of our routine activities cannot be done without the active participation of our hands.
A human hand is divided into several parts:
1. Finger
2. Palm
3. Opisthenar (back of the palm)
4. Wrist
5. Forearm.
When your hand suffers any injury or medical condition that affects the blood supply in your hand, there are chances that you might develop an infection in the injured area of your hand.
When these wounds or injuries are not given immediate medical attention and appropriate treatment, the open wound might get infected soon after coming in contact with bacteria or viruses in the atmosphere, resulting in a hand infection.
Hand infections are frequently diagnosed clinically. The diagnosis of a hand infection typically involves a physical examination and medical history review by a doctor. The following tests may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis:
Based on the results of these tests, the doctor can determine the type of infection and the best course of treatment. It's essential to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you have a hand infection.
An infection of the eponychium that is the epidermis bordering the nail is called Paronychia. It causes inflammation, erythema, and pain at the lower end of the fingernail. In general, trauma around the tip of the finger results in Acute Paronychia.
This infection could be an outcome of a manicure, an ingrown nail, or dishwashing, which usually becomes evident within the first week of trauma. In children, it usually takes place because of thumb sucking. Soaking in warm water may help you solve the problem unless an abscess hasn't developed; otherwise, it has to be drained with an incision.
It is a form of abscess of the phalanx pad, that occurs in the fingertips. Felon is usually caused when bacteria enters a fingertip through a puncture wound. The thumb and index finger are the ones that are mainly affected by this acute infection.
It may also occur when the paronychia is left untreated and spreads into the fingertip pad. The medical condition causes excruciating pain, and the swelling may result in tissue necrosis. It is possible to treat it with antibiotics, elevation, and saline soaks only if it's diagnosed at an early stage.
Viral hand infections, except for 'herpetic whitlow,' are uncommon. This medical condition is an outcome of the 'type 1 or 2 herpes simplex virus' entering the broken skin.
Individuals exposed to oral secretions might be at a higher risk if they do not use appropriate precautions. Erythema, edema, tenderness, etc., in the infected finger are signs and symptoms of Herpetic Whitlow. Tzanck test, DNA amplification technique, or viral culture might be opted for to help diagnose herpes simplex virus.
Tendons that are responsible for the bending and movement of fingers are present in the hand, pass through the palm, and reach into the fingertips. These flexor tendons enter a sheath at the base of the finger. The flexor tendon canal might get infected by a cut or scratch on the palm side near a joint.
This infection can cause severe stiffness and excruciating pain and destroy the affected tendon, which requires immediate medical attention. IV antibiotics and surgical treatment are required as part of the treatment.
It is a skin infection that results in pain, warmth, and skin redness. Patients who suffer from cellulitis might have a fever, chills, or feel ill. It usually takes place in the surrounding area of a cut/break in the skin.
It has the ability to spread in the injured limb or bloodstream very rapidly, due to which it requires prompt treatment. In most cases, antibiotics are used as a method of treatment. At the same time, surgical drainage is only chosen when an abscess is developed beneath the skin.
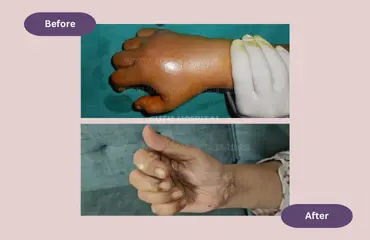
Hand infections can have dire consequences such as excruciating pain, tenderness, swelling, abscess, inability to perform actions with the infected limb, etc., that can last for a long time and, in some instances, even after the infection has been treated. In most cases, hand infections that do not require surgery and those with mild severity are usually treated with IV antibiotics and painkillers to reduce pain, tenderness, and inflammation.
Treatment for hand infections depends on the type and severity of the infection. Common treatments include, in terms of non-surgical methods:
Non-surgical methods
Surgical Methods
However, if an abscess is developed beneath the skin or on the surface, it might require surgical drainage. In the surgical procedure, the doctor makes an incision in the skin, and all the infected blood and pus are removed through that incision.
But surgery might not be necessary if the infection is diagnosed at an early stage. However, there are certain infections that might cause permanent damage if not treated with an appropriate combination of antibiotics and surgery. It is essential to remove the infected, dead, or devitalized tissue from the body to prevent the infection from spreading.
Eye-to-detail: Cutis Hospital is enriched with experienced and specialized hand surgeons who are knowledgeable in the latest techniques for effective hand infection treatment in patients. They abide by stringent protocols as guidelines for infection control to minimize the risk of infection during and after treatment.
Tech-driven: Cutis Hospital has access to up-to-date diagnostic tools, such as imaging equipment and laboratory facilities, to accurately diagnose hand infections and monitor the healing process effectively, leading to satisfactory results. We even have a well-stocked pharmacy to provide patients with appropriate medications, antibiotics, and pain relief options.
Top-notch patient care: Our team follows clean and sterilized surgical facilities to prevent infections from spreading during treatment, resulting in top-notch patient care, diagnosis and treatment. We offer an end-to-end commitment to patient satisfaction, followed by open communication and ongoing follow-up care to ensure the best possible outcome for patients.
Personalized treatment: The experts at Cutis have knowledge regarding all types of hand infections and know what kind of treatment would be better based on the type of infection. They even provide complete access to physical therapy and rehabilitation services to help patients regain full use of their hands after treatment.

Cutis Hospital is conveniently located in Ghatlodia, Ahmedabad, making it easily accessible via multiple modes of transportation. Below are the various ways you can reach our facility:
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport: Located approximately 12.7 km from Cutis Hospital, offering convenient access for patients traveling from outside the city.
Chandlodiya Railway Station: Approximately 2.4 km from Cutis Hospital.
Ahmedabad Railway Station: Around 11 km from our center.
GSRTC:
Ahmedabad Central Bus Station (GSRTC): About 10.3 km from the hospital.
AMTS:
Bhuyangdev Cross Road Bus Stop: Just 500 meters from Cutis Hospital.
BRTS:
Bhuyangdev BRTS Bus Stop: Only 170 meters from our center.
We provide effective surgical and non-surgical treatments for all parts of the body. At Cutis Hospital, our cosmetic and plastic surgery team is committed to giving patients safe and high-quality care.