Leg/foot ulceration may result from:
The treatment and management of foot ulcers and infections depend upon the type of infection. However, the following methods are used to treat most leg and foot ulcers:
The goal of treatment for leg and foot infections or ulcers is to relieve pain and ensure proper wound healing and speedy recovery. At Cutis, experienced medical professionals can create a personalized treatment plan based on the severity and type of ulcer along with a patient’s health condition.
We have a sanitized set-up to prevent infection and use advanced tools to ensure the best outcome.
Foot infections and ulcers need immediate care to prevent advancement. We have skilled doctors at Cutis. Book a consultation now!
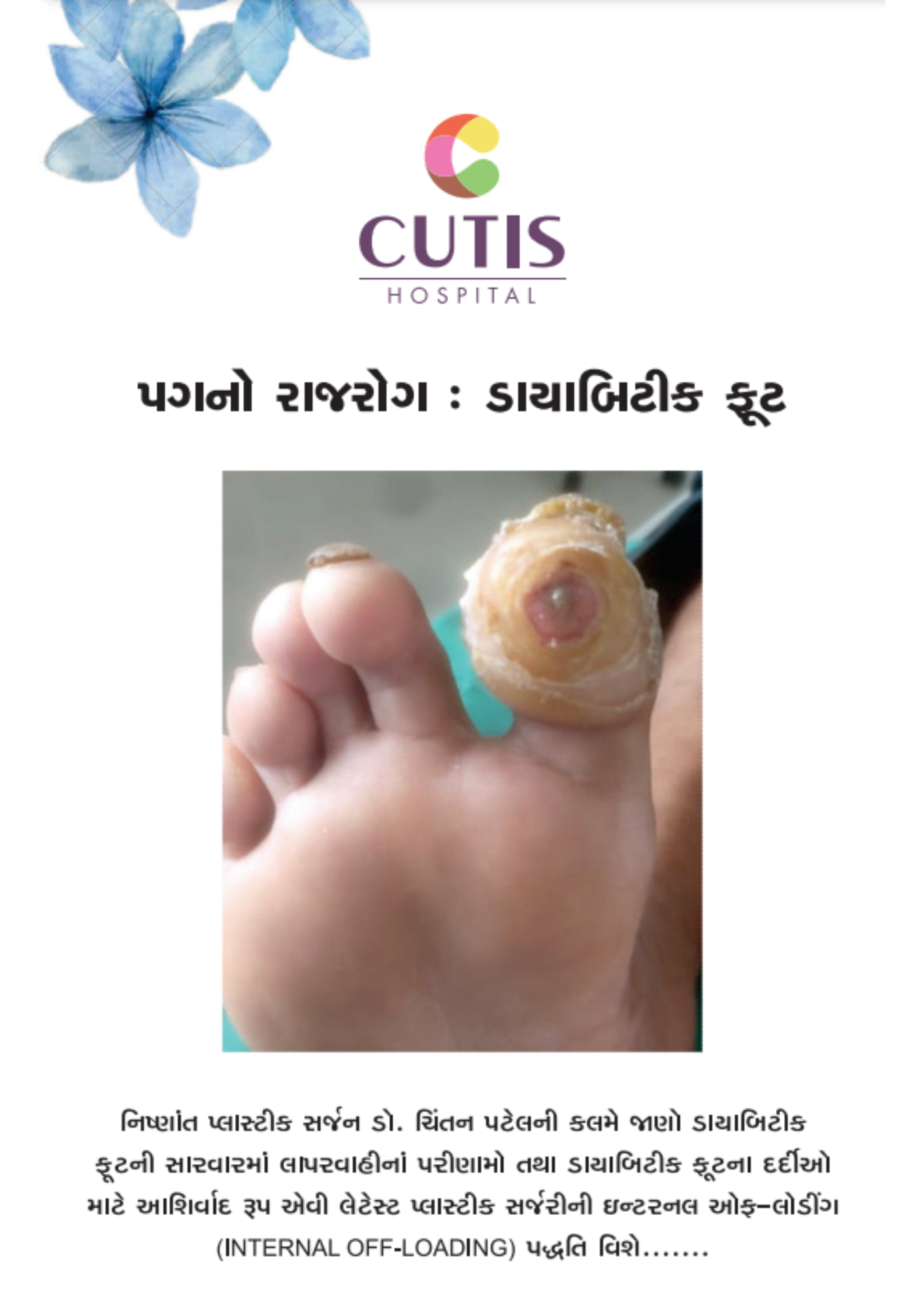
Common symptoms of foot infection:
Foot blisters are pockets of clear fluid. However, infected foot blisters release yellowish/greenish pus. There may be warmth and redness around infected blisters.
Redness of skin at the site of infection.
The infected area may feel warm to the touch.
Common symptoms of foot ulcers
There are three common types of leg and foot ulcers.
Venous stasis ulcers
Neurotrophic (diabetic)
Arterial (ischemic) Ulcers
At Cutis, specialist doctors evaluate a patient’s complete medical history and thoroughly examine the wound in order to determine the stage of leg & foot ulcers or infection. A personalized treatment plan is developed depending upon a patient’s health condition and the outcome of medical imaging studies, such as MRI/CT-scan/x-ray or non-invasive vascular studies.
Treatment for leg/foot infections or ulcers depends upon the type and stage of the ulcer or infection. It also depends upon a patient’s health, additional medical conditions and the ability to take care of the wound. However, the goal of treatment remains the same in all scenarios.
Pain relief
Speedy recovery
Wound healing
Foot Infection Treatments
Treatment for Severe Infection
Foot Ulcer Treatment
Treatment for Venous Ulcer
Venous ulcers are treated with compression of the ulcerated leg to minimize oedema and swelling. A doctor may use compression stockings, multi-layer compression wraps or ACE bandage for the treatment. The compression treatment is applied from the toes or foot to the area below the knee. The following medicated dressings are also used for treatment.
Treatment for Arterial Ulcer
It may become necessary to perform endovascular therapy or bypass surgery to restore blood circulation to the affected leg. The goal of arterial ulcer treatment is as follows:
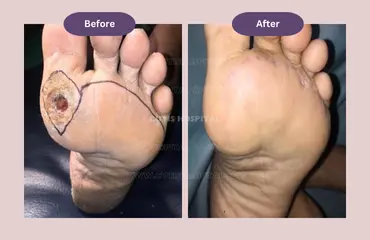
Treatment for Neurotrophic Ulcers
Yes. It is possible to prevent the ulcer from aggravating in the following manner:.
It is possible to prevent a sore from becoming an ulcer through appropriate foot care.
At Cutis, an experienced surgeon may perform foot infection surgery in the following scenarios:
Cutis Hospital is conveniently located in Ghatlodia, Ahmedabad, making it easily accessible via multiple modes of transportation. Below are the various ways you can reach our facility:
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport: Located approximately 12.7 km from Cutis Hospital, offering convenient access for patients traveling from outside the city.
Chandlodiya Railway Station: Approximately 2.4 km from Cutis Hospital.
Ahmedabad Railway Station: Around 11 km from our center.
GSRTC:
Ahmedabad Central Bus Station (GSRTC): About 10.3 km from the hospital.
AMTS:
Bhuyangdev Cross Road Bus Stop: Just 500 meters from Cutis Hospital.
BRTS:
Bhuyangdev BRTS Bus Stop: Only 170 meters from our center.
We provide effective surgical and non-surgical treatments for all parts of the body. At Cutis Hospital, our cosmetic and plastic surgery team is committed to giving patients safe and high-quality care.