Warts are (generally) harmless skin growths caused by infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are characterized by the development of small, rough, and raised bumps on the skin. Warts can occur in various parts of the body and are common in people of all ages, although they are most commonly observed in children and young adults.
HPV, the virus responsible for warts, enters the body through cuts or breaks in the skin. The immune system typically helps to eliminate the virus, but in some cases, the virus can lead to the formation of warts.
Wart removal surgery includes physically removing or destroying warts, which are harmless skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus.
In certain situations, warts can be unpleasant and create additional complications. Certain warts might be malignant, in which case they should be removed very once to lessen the chance that they will spread. In these circumstances, surgery is usually the most effective treatment option.
Wart removal surgery is advantageous since it allows for the rapid elimination of warts. When it comes to warts that are resistant to non-invasive treatment, surgery is a successful treatment option. Furthermore, it is a one-time surgery that produces quick and effective results. However, wart removal surgery might occasionally result in a scar.
A dermatologist can identify if you have a wart by looking at it. In rare circumstances, a dermatologist may need to do a skin biopsy to be certain.
If a dermatologist needs to do a biopsy, it involves eliminating a small part of the wart (a shave biopsy) and submitting it to a laboratory for investigation to rule out other types of skin growth. A biopsy is a rapid and safe technique that dermatologists can do. It should not cause any distress.
To look for dark, pinpoint spots, or occluded blood vessels, which are frequently seen in warts, they can further examine the wart by scraping off its top layer.
The appearance of a wart is determined by its type. There are various kinds of warts:
Warts are your body's response to the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is infectious and spreads by direct contact with a wart or anything that has touched it.
Nevertheless, it may take several months or even a year for the wart to initially appear. Although anybody can develop a wart, children and teenagers, individuals with compromised immune systems, and those who bite or scratch at their hangnails are the most susceptible.
Your doctor may recommend one of the following treatments based on the location of your warts, the signs, and your preferences. These techniques are occasionally used in conjunction with home remedies.
Stronger peeling agent (salicylic acid). Salicylic acid-based prescription-strength wart treatments function by gradually eliminating a wart's layers. According to studies, freezing and salicylic acid work better together.
Freezing (Cryotherapy): Freezing. At a doctor's office, freezing therapy entails applying liquid nitrogen to your wart. The way freezing works is that it forms a blister around and under your wart. After a week or so, the dead tissue sloughs off. This technique may help activate your immune system to combat viral warts. You'll probably need to repeat treatments to see better results.
Other acids: In case freezing or salicylic acid doesn't work, your doctor might attempt trichloroacetic acid. In this procedure, the physician uses a wooden toothpick to apply the acid after shaving the wart's surface. It requires weekly treatments, and you may have side effects such as burning and stinging.
Minor surgery: If any of the home remedies or treatments do not work, your doctor can perform a little surgery to remove the irritating tissue. It could leave a scar in the treated area.
Laser therapy. The pulsed-dye laser therapy damages microscopic blood vessels. The diseased tissue finally dies, and the wart goes away. There is limited evidence that this procedure is successful, and it can cause discomfort and damage.
It's important to note that the vast majority of warts are benign and do not lead to serious health problems. However, certain risk factors and potential complications associated with warts include:
Cutis Hospital is a renowned hospital offering a wide range of treatment options for diverse problems. Here are some of the reasons why you should go to Cutis Hospital to get the best Cyst removal surgery:
Top Healthcare Professionals: Our skilled team comprises experienced surgeons and specialists, ensuring expert care and personalized attention throughout your cyst removal treatment with us.
Post-Operative Support: Beyond surgical intervention, our commitment extends to comprehensive post-operative support. Our healthcare professionals guide you through recovery, ensuring optimal healing and long-term success.
Individualized Treatment Plans: Recognizing each patient's unique needs, we craft individualized treatment plans. Our cyst removal treatment is tailored to address specific fractures, ensuring the best and most satisfactory outcomes.
State-of-the-Art Facilities: Cutis Hospital is equipped with modern and advanced facilities, including cutting-edge technology for diagnostic assessments and surgical procedures.
We prioritize excellence, comfort, and well-being for personalized wart removal treatment!
Book an appointment with our experts!

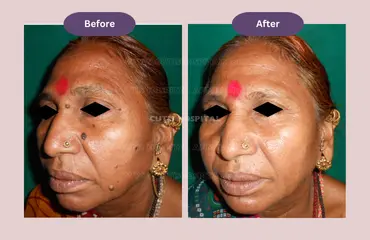
Most warts will eventually disappear without treatment. Without therapy, about 90% of warts in children will go away in two years, and half will disappear in six months. It may take longer for adults.
You should consult a doctor when,
Many patients frequently misidentify warts as skin lesions. Although they are both skin conditions, warts and skin lesions are not the same. Skin lesions occur when a section of skin seems lumpy or painful and changes in color and appearance relative to the surrounding area. Skin lesions may indicate a possible case of skin cancer.
In contrast, warts are rough-textured skin growths that result from the human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Warts’ appearance can also be influenced by their location on the body. The appearance of the wart changes depending on the thickness of the skin in different areas.
The wart virus has no known treatment. Warts might resurface at any time, at a different location, or in the same spot. Treating warts as soon as they emerge is the most effective approach to keep them under control.
But, the following advice can assist you in preventing them from occurring in the first place or halting their spread:
It’s not always possible to say goodbye to warts permanently, even after they’ve been removed. Warts exist because of the HPV virus, and approximately 80% of people contract the virus again at some point.
The postoperative techniques vary according to the type of operation, but some will apply to either:
As you treat your warts, you will gain from strengthening your immune system by eating foods high in zinc, such as chickpeas and pumpkin seeds, and foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and strawberries. Green leafy vegetables, as well as probiotic meals like live-culture yogurt and raw cheese, are beneficial to your health.
Cutis Hospital is conveniently located in Ghatlodia, Ahmedabad, making it easily accessible via multiple modes of transportation. Below are the various ways you can reach our facility:
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport: Located approximately 12.7 km from Cutis Hospital, offering convenient access for patients traveling from outside the city.
Chandlodiya Railway Station: Approximately 2.4 km from Cutis Hospital.
Ahmedabad Railway Station: Around 11 km from our center.
GSRTC:
Ahmedabad Central Bus Station (GSRTC): About 10.3 km from the hospital.
AMTS:
Bhuyangdev Cross Road Bus Stop: Just 500 meters from Cutis Hospital.
BRTS:
Bhuyangdev BRTS Bus Stop: Only 170 meters from our center.
We provide effective surgical and non-surgical treatments for all parts of the body. At Cutis Hospital, our cosmetic and plastic surgery team is committed to giving patients safe and high-quality care.